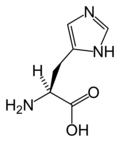

Basic amino acid His H RNA code: CAU, CAC
Histidine's imidazole side chain has a hydrogen-bound nitrogen atom that is slighty acidic and another nitrogen that is slightly basic. The almost neutral pKa of histidine ensures that its charge will change in response to relatively small shifts in cellular pH.
Histidine functions as a co-ordinating ligand in metalloproteins, and at the catalytic site of some enzymes. In catalytic triads, the basic nitrogen of histidine extracts a proton from serine, threonine or cysteine, activating the nitrogen as a nucleophile. In a histidine proton shuttle, histidine rapidly shuttles protons by abstracting a proton onto the basic nitrogen to generate a positively-charged intermediate before passing a proton from the acidic nitrogen. Carbonic anhydrases employ the histidine proton shuttle to rapidly shuttle protons away from a zinc-bound water molecule to quickly regenerate the active form of the enzyme.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.